The question of whether Oracles –— or just keeping an AGI forcibly confined -— are safer than fully free AGIs has been the subject of debate for a long time. Armstrong, SandbergSandberg, and Bostrom discuss Oracle safety at length in their Thinking inside the box: using and controlling an Oracle AI. In the paper, the authors review various methods which might be used to measure an Oracle's accuracy. They also try to shed some light on some weaknesses and dangers that can emerge on the human side, such as psychological vulnerabilities which can be exploited by the Oracle through social engineering. The paper discusses ideas for physical security (“boxing”), as well as problems involved with trying to program the AI to only answer questions. In the end, the paper reaches the cautious conclusion ofthat Oracle AIs are probably being safer than free AGIs.
In a related work, Dreams of Friendliness, Eliezer Yudkowsky gives an informal argument stating that all oracles will be agent-like, that is, driven by its own goals. He rests on the idea that anything considered "intelligent" must choose the correct course of action among all actions available. That means that the Oracle will have many possible things to believe, although very few of them are correct. ThereforeTherefore, believing the correct thing means some method was used to select the correct belief from the many incorrect beliefs. By definition, this is an optimization process which has a goal of selecting correct beliefs.
One can then imagine all the things that might be useful in achieving the goal of "have"having correct beliefs". For instance, acquiring more computing power and resources could help this goal. As such, an Oracle could determine that it might answer more accurately and easily to a certain question if it turned all matter outside the box to computronium, therefore killing all the existing life.
Given that true AIs are goal-oriented agents, it follows that a True Oracular AI has some kind of oracular goals. These act as the motivation system for the Oracle to give us the information we ask for and nothing else.
This means that a True Oracular AI has to have a full specification of human values, thus making it a FAI-complete problem – if we could achieve such skill and knowledgeknowledge, we could just build a Friendly AI and bypass the Oracle AI concept.
Any system that acts only as an informative machine, only answering questionsquestions, and has no goals is by definition not an AI at all. That means that a non-AI Oracular is but a calculator of outputs based on inputs. Since the term in itself is heterogeneous, the proposals made for a sub-division are merely informal.
An Advisor can be seen as a system that gathers data from the real world and computes the answer to an informal “what we ought to do?” question. They also represent aan FAI-complete problem.
Finally, a Predictor is seen as a system that takes a corpus of data and produces a probability distribution over future possible data. There are some proposed dangers with predictors, namely exhibiting goal-seeking behavior which does not converge with humanityhumanity's goals and the ability to influence us through the predictions.
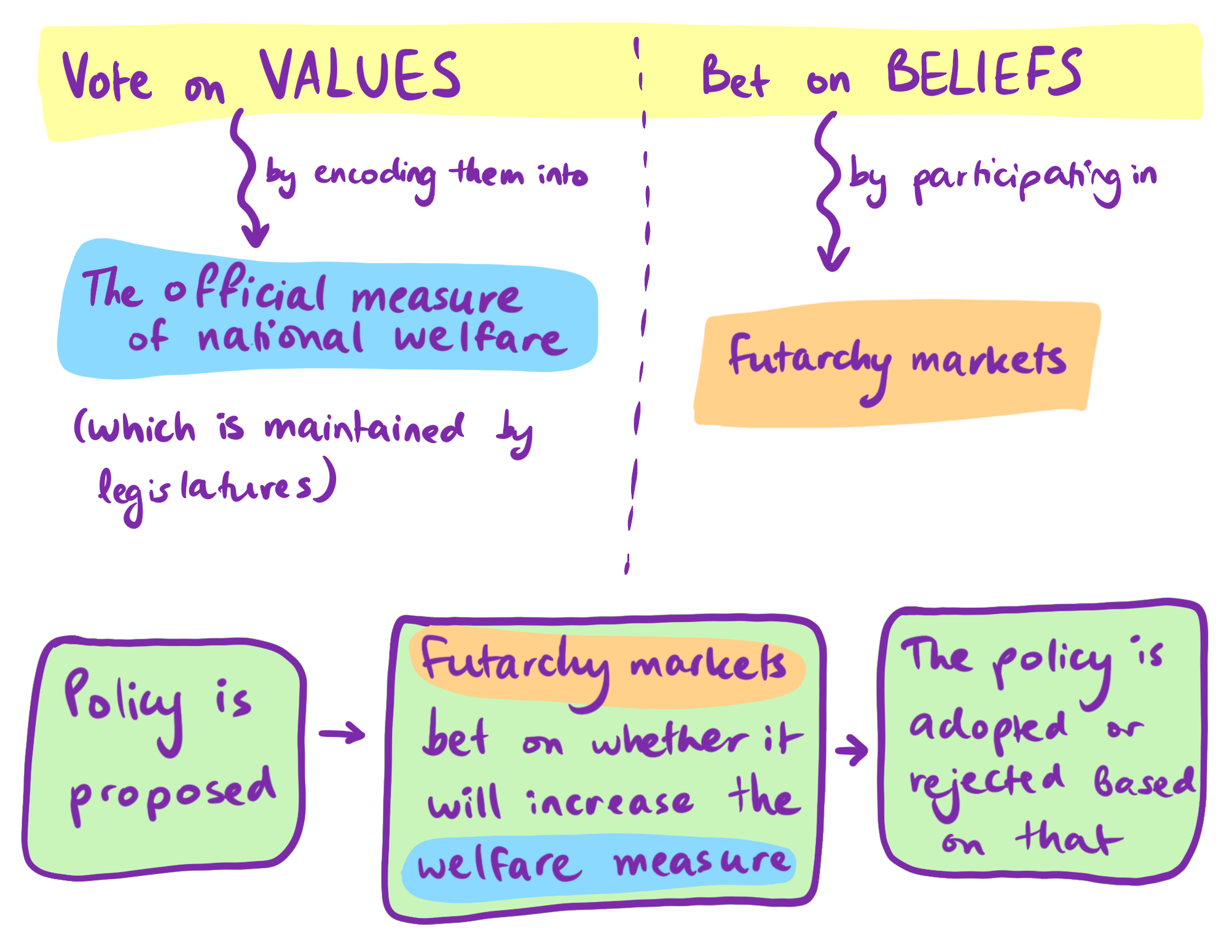
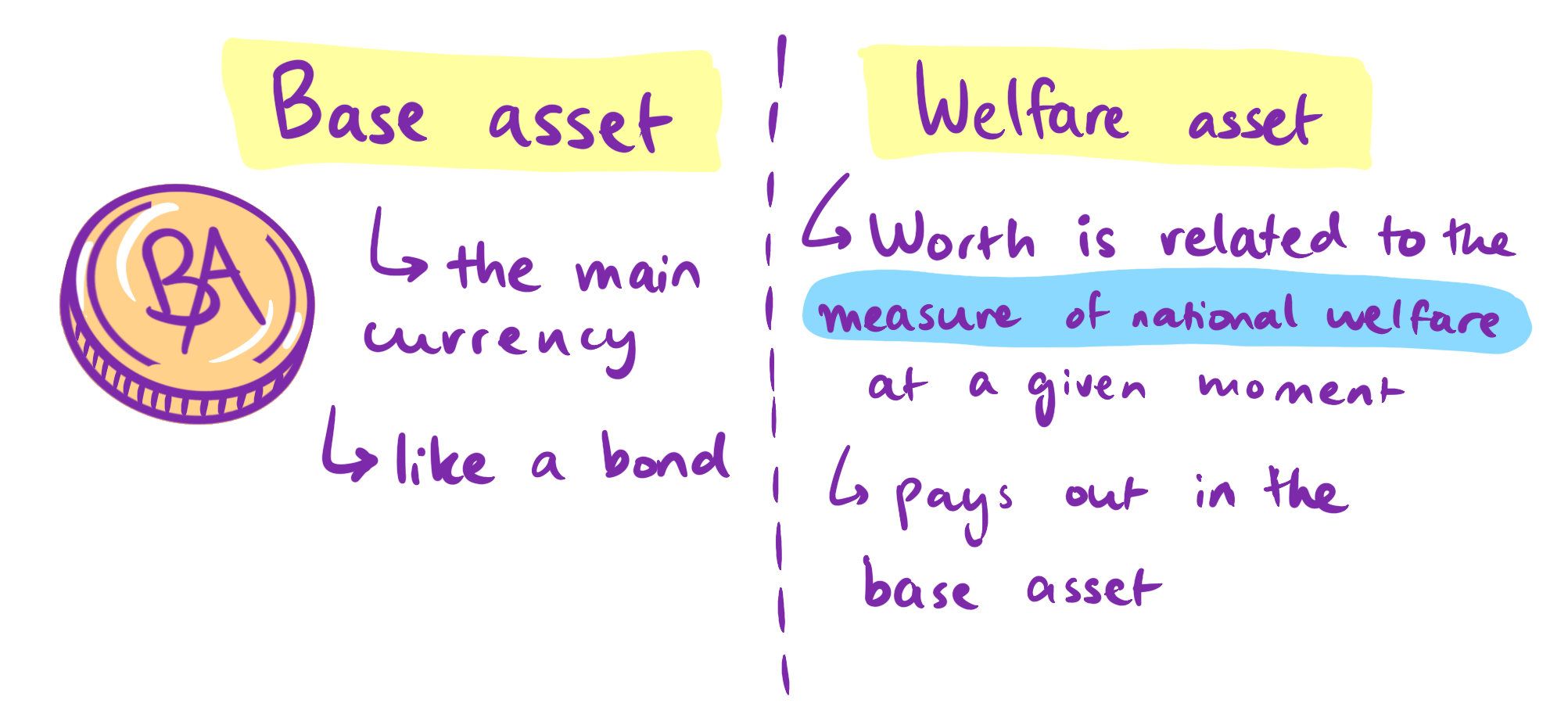


"Current," here, is indexed to a decade ago, and can no longer be claimed confidently.